 login/create account
login/create account
Degenerate colorings of planar graphs
A graph 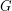 is
is 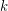 -degenerate if every subgraph of
-degenerate if every subgraph of 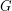 has a vertex of degree
has a vertex of degree 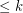 .
.
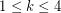 , the union of any
, the union of any 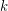 color classes induces a
color classes induces a 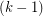 -degenerate graph.
-degenerate graph. An acyclic coloring of a graph 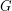 is a proper coloring with the added property that the union of any two color classes induces a forest. Grunbaum famously conjectured that every simple planar graph has an acyclic 5-coloring. Following a sequence of partial results, Borodin [B] resolved this conjecture with an impressive and detailed argument. In the same paper, Borodin made the above conjecture, which, if true, would give a stronger result (as forests are precisely the 1-degenerate graphs).
is a proper coloring with the added property that the union of any two color classes induces a forest. Grunbaum famously conjectured that every simple planar graph has an acyclic 5-coloring. Following a sequence of partial results, Borodin [B] resolved this conjecture with an impressive and detailed argument. In the same paper, Borodin made the above conjecture, which, if true, would give a stronger result (as forests are precisely the 1-degenerate graphs).
A degenerate coloring of a graph 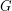 is a proper coloring with the added property that the union of any
is a proper coloring with the added property that the union of any 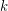 color classes induces a
color classes induces a 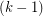 -degenerate graph. A planar graph of minimum degree 5 cannot have a degenerate 5-coloring, but if the above conjecture holds, something just short of this is true. Rautenbach [R] proved that every planar graph has a degenerate 18-coloring, and recently, Mohar, Spacepan, and Zhu showed that every planar graph has a degenerate 9-coloring.
-degenerate graph. A planar graph of minimum degree 5 cannot have a degenerate 5-coloring, but if the above conjecture holds, something just short of this is true. Rautenbach [R] proved that every planar graph has a degenerate 18-coloring, and recently, Mohar, Spacepan, and Zhu showed that every planar graph has a degenerate 9-coloring.
Bibliography
*[B] O. V. Borodin, A proof of B. Grünbaum's conjecture on the acyclic  -colorability of planar graphs. Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR 231 (1976), no. 1, 18--20. MathSciNet
-colorability of planar graphs. Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR 231 (1976), no. 1, 18--20. MathSciNet
[R] D. Rautenbach, A conjecture of Borodin and a coloring of Grünbaum. Fifth Cracow Conference on Graph Theory USTRON '06, 187--194 Electron. Notes Discrete Math., 24, Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2006.
* indicates original appearance(s) of problem.

 Drupal
Drupal CSI of Charles University
CSI of Charles University